
Ultimate Guide to Energy-Efficient Prefab Tiny Homes

Nomad Adjacent2 months ago
Ultimate Guide to Energy-Efficient Prefab Tiny Homes
Prefab tiny homes are small, factory-built homes (120–800 sq. ft.) designed for quick setup and energy savings. They combine high-quality insulation, airtight construction, and renewable energy systems like solar panels to cut energy use by up to 88% and carbon emissions by 96%. These homes cost less to operate, with utility savings of 60–90%, and can achieve net-zero energy. Prices start around $35,000, but energy-efficient models may cost $170,000–$260,000. Federal and state incentives, such as tax credits for solar panels and heat pumps, make them more affordable. Prefab construction also reduces waste and speeds up delivery, making them ideal for minimalists, off-grid living, or as accessory units. Before buying, check local regulations and ensure the home meets energy standards like ENERGY STAR or Passive House.
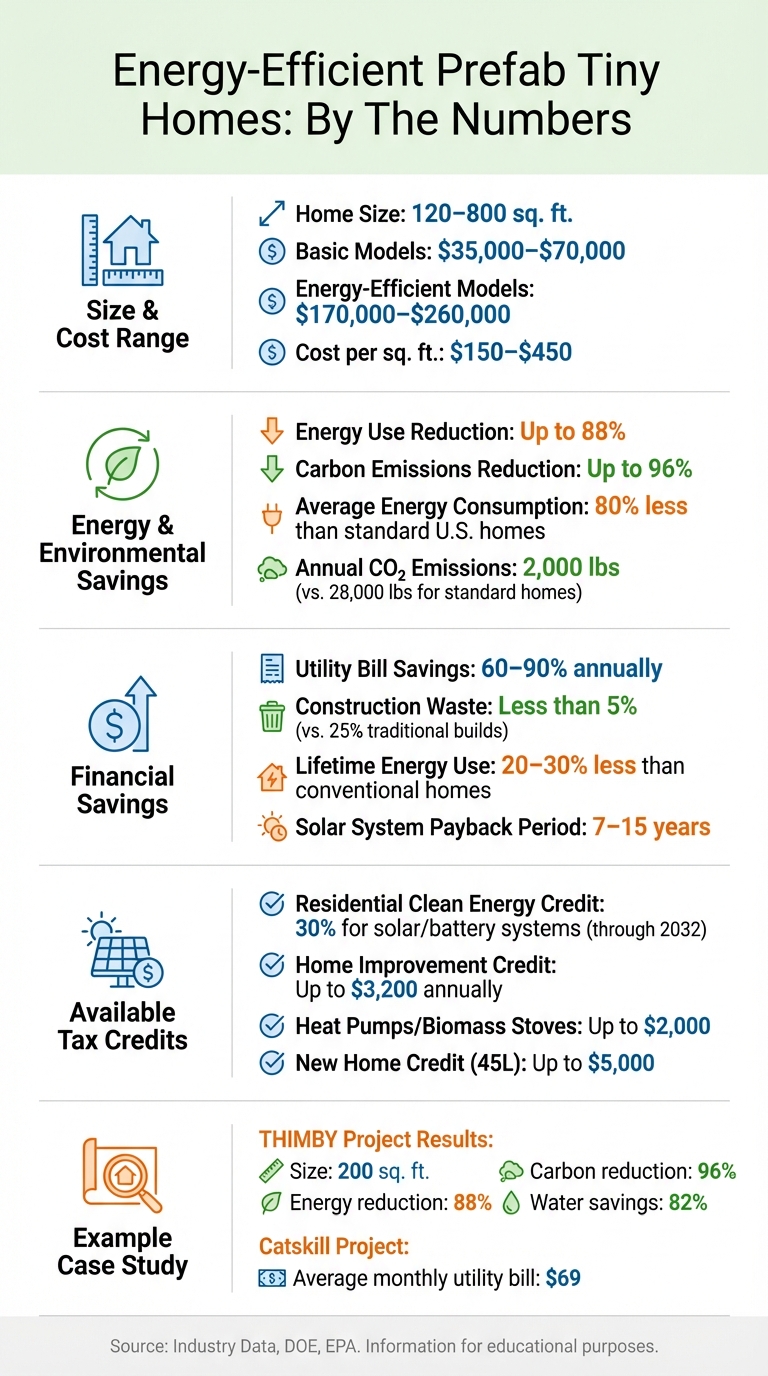
Energy-Efficient Prefab Tiny Homes: Cost Savings and Environmental Impact Statistics
15 Affordable Prefab Tiny Houses You Can Buy Under $50,000 from Amazon and Wayfair
Key Features of Energy-Efficient Prefab Tiny Homes
Energy-efficient prefab tiny homes combine three key systems to reduce energy consumption while ensuring comfort year-round: high-performance insulation and windows, integrated renewable energy systems, and smart energy management technology. Let’s break down how each of these components works.
Insulation and Energy-Efficient Windows
Think of the building envelope as your home’s armor against energy loss. Prefab tiny homes often use Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs), which combine structural support and rigid insulation in one factory-cut piece. This design minimizes thermal bridging - those pesky spots where heat escapes - and speeds up construction time.
For even higher insulation performance, spray foam or insulated sheathing is common. In older prefab homes, retrofitting with solutions like belly wraps, insulated skirting, or roof caps can significantly cut down heat loss.
Windows are another big player in energy efficiency. Advanced windows with low-e coatings and optimized U-values and Solar Heat Gain Coefficients (SHGC) help retain warmth during winter while avoiding overheating in summer. A great example is the Project ZeNETH team at Western Washington University. In November 2025, they built a ~250-square-foot net-zero tiny home featuring German-engineered Innotech windows paired with SIPs. Their design, validated with Egauge monitoring, showcased how a well-sealed envelope could support a 5 kW solar array and a Tesla Powerwall.
To ensure airtight construction, builders use specialized tapes, gaskets, and splines to seal every joint and penetration. Blower-door testing is also essential - it identifies leaks early, when repairs are still manageable.
"Blower-door testing before finishes finds leaks when fixes are easy." - Articru Scribes, Zero-Energy Tiny House Guide
This airtight foundation is critical for reducing energy loss and sets the stage for efficient renewable energy integration.
Renewable Energy Systems
Once the building envelope is optimized, renewable energy systems take center stage. Tiny homes, with their smaller energy needs, allow for more manageable and cost-effective renewable setups.
Most systems include solar panels, inverters, and battery storage. Microinverters can boost panel efficiency even in shaded conditions, while integrated battery storage systems reduce upfront costs. Studies show that improving a home’s insulation and sealing reduces energy demand, allowing for smaller and more affordable renewable systems.
To further enhance efficiency, many tiny homes use mini-split heat pumps, which are up to 60% more efficient than traditional heating systems. A well-matched solar array and battery system can slash utility bills by 60% to 90%, with payback periods ranging from 7 to 15 years. Before installing a renewable system, it’s smart to conduct a load audit - use manufacturer calculators to estimate seasonal energy consumption and ensure the system fits your actual needs.
Smart Home Technology for Energy Management
Smart technology ties everything together by optimizing energy use. Tools like Egauge circuit-level monitoring provide real-time data, helping you adjust your energy consumption based on accurate insights.
Programmable thermostats and occupancy sensors adjust heating, cooling, and lighting automatically. For instance, motion sensors in hallways and bathrooms ensure lights aren’t left on unnecessarily. LED bulbs, which last up to 50 times longer than incandescent ones, complement these systems perfectly.
Smart scheduling can also align energy use with solar peaks. For example, you can set your dishwasher to run during periods of maximum solar output, reducing battery strain and extending its lifespan.
"Optimizing such houses through integration of energy and water saving technologies, home energy management systems, and strong communication between modelers, builders and occupants will be essential to achieving dramatic energy (87%), water (82%), and carbon (96%) savings." - Alana Bowen Siegner, UC Berkeley THIMBY project
To keep everything running smoothly, it’s important to regularly update firmware and clean filters. These small steps ensure your smart systems and renewable setups continue to perform efficiently.
Design and Customization Options
Energy-efficient prefab tiny homes show how smart design can blend comfort and efficiency seamlessly. The secret lies in combining passive strategies, adaptable layouts, and sustainable materials to create spaces that feel open and inviting while keeping energy use to a minimum.
Modular Layouts for Space Efficiency
Prefab construction shines when it comes to flexibility. Sliding partitions can turn a living room into a cozy bedroom, while foldable furniture and built-in storage make the most of every square inch. This approach, often called thermal zoning, focuses high-activity areas in a warm core, using storage or service zones as buffers to maintain stable interior temperatures.
One of the best parts of prefab homes is the ability to customize the layout during the factory build phase. Need a home office? Extra closet space? These tweaks are easier - and cheaper - when planned ahead of assembly. Plus, the precision of factory construction ensures that walls, floors, and ceilings align perfectly, minimizing gaps that could waste energy. This thoughtful design approach complements the energy-saving features mentioned earlier, laying the groundwork for efficient natural lighting and ventilation.
Natural Lighting and Ventilation Strategies
Good design doesn't stop at layout; natural lighting plays a big role in energy efficiency. Passive solar orientation is a game-changer. By aligning your home’s long axis within 30 degrees of true south, you can capture the low winter sun while roof overhangs block the harsh summer rays. South-facing, triple-pane windows flood interiors with daylight, cutting down on the need for artificial lighting.
Ventilation is equally important. Cross-ventilation and the stack effect - where warm air rises and escapes through skylights or high vents - help keep your home cool without relying on air conditioning. A great example of this is the Catskill Project in Livingston Manor, New York. This 25-unit carbon-neutral community, completed in April 2024, used prefab components from Bensonwood, triple-pane Unilux windows, and Zehnder Q350 Energy Recovery Ventilators. According to developer Greg Hale, the first model home averaged a $69 monthly utility bill over two years.
"The precision possible in Bensonwood's factory makes Passive House performance a replicable outcome instead of an exceptional achievement." - Greg Hale, Co-founder and Principal, Manor Falls Associates
Strategically placed windows also help manage moisture, which is crucial in airtight tiny homes where condensation can lead to mold issues. Operable windows make nighttime cooling easier, reducing the strain on your mini-split heat pump during warmer months.
Eco-Friendly Building Materials
To round out the design, eco-friendly materials enhance both performance and sustainability. Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) offer high insulation (R-value) and reduce thermal bridging, combining structure and rigid insulation while generating less than 5% construction waste. For even better insulation, straw-bale construction provides R-40 walls with excellent soundproofing, all while using agricultural byproducts and keeping embodied carbon low.
Bamboo brings hurricane-level structural strength and absorbs carbon. Other options like reclaimed wood, salvaged brick, and recycled-content insulation help shrink your home’s carbon footprint. Pam Hutter, Principal Architect at Hutter Architects, sums it up well:
"The most sustainable square foot is the one you don't build." - Pam Hutter, Principal Architect, Hutter Architects
For finishing touches, low-VOC paints, sealants, and adhesives are a must to maintain good air quality in your compact, airtight space. Light-reflective surfaces on walls and ceilings can also amplify natural daylight, making small spaces feel bigger while cutting down on electricity use. These material choices not only enhance energy performance but also streamline factory construction. Prefab builds typically generate less than 5% material waste - compared to 25% for traditional builds - and use 20% to 30% less energy over their lifetime.
| Material/Strategy | Performance Impact | Sustainability Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| SIPs | High R-value, reduced thermal bridging | Less than 5% construction waste |
| Bamboo | Hurricane-rated structural strength | Carbon sequestration |
| Straw-Bale | R-40 insulation; soundproofing | Low embodied carbon |
| Low-VOC Finishes | Better indoor air quality | Reduced off-gassing |
| Living Roofs | Natural thermal mass/insulation | Stormwater management |
sbb-itb-718b9e4
Costs and Long-Term Savings
Energy-efficient prefab tiny homes may have a higher upfront cost, but their monthly savings and available incentives can make them an appealing financial choice. Let’s break down the expenses - from purchase price to long-term utility savings - so you can make an informed decision.
Purchase Costs and Financing
The price range for prefab tiny homes varies significantly. Basic models start between $30,000 and $70,000, while energy-efficient designs from specialized manufacturers can cost $170,000 to over $260,000. For instance, the Plant Prefab LivingHome 10 is priced at $180,000, and Method Homes' M Series starts at $170,000.
Interestingly, the cost per square foot for tiny homes - ranging from $150 to $450 - is often higher than that of traditional homes, which average $150 to $200 per square foot. This is because fixed expenses, like kitchens and HVAC systems, are spread over a smaller area. A more budget-friendly option could be purchasing a "shell" (finished exterior but unfinished interior), which starts at $4,000 to $15,000, allowing for personalized, energy-efficient interior upgrades.
Additional costs like site preparation, utility hookups, and permits can add up quickly. These expenses typically range as follows:
- Site preparation and utility hookups: $3,000 to $25,000
- Delivery fees: $200 to $5,000
- Building permits: $500 to $3,100
These costs are usually not included in the base price, so it’s smart to set aside extra funds for these necessities.
Financing a tiny home often requires creative solutions since traditional mortgages don’t typically apply. Buyers frequently turn to personal loans, which usually have interest rates 2% to 5% higher than mortgages, or RV loans for certified mobile units. Another option is a home equity line of credit. Energy Efficient Mortgages (EEMs) can also provide additional funds - typically $3,000 to $6,000 - by factoring in projected energy savings. If your tiny home requires a permanent foundation, expect to pay between $3,000 and $15,000.
While the initial costs may seem steep, the ongoing savings can make these homes a worthwhile investment.
Monthly Energy Savings
Tiny homes are known for their impressive energy efficiency. On average, they consume 80% less energy than traditional U.S. homes. High-performance models with airtight construction and superior insulation can even achieve net-zero energy, leading to a $0 energy bill.
"The average tiny house uses 80% less energy than a standard U.S. home, and total costs range from $30,000 to $150,000, potentially saving hundreds of thousands compared to traditional housing." - TenantCloud Team
Take the THIMBY project as an example. This 200-square-foot tiny home in California reduced its energy use by 88% and cut carbon emissions by 96% compared to a 2,100-square-foot home built to 2016 Title 24 standards.
After applying state and federal incentives, the cost premium for energy-efficient features typically decreases to just 4% to 8%. Over time, the energy savings often outweigh the higher initial investment, reducing the total cost of ownership.
Tax Credits and Government Incentives
Federal and state incentives further enhance the affordability of energy-efficient tiny homes. For example, the Residential Clean Energy Credit (Section 25D) offers a 30% credit for investments in renewable energy systems like solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage through 2032. This credit has no annual or lifetime cap. After applying this credit, the cost of solar panel installations for tiny homes typically falls between $3,500 and $8,800.
The Energy Efficient Home Improvement Credit (Section 25C) provides up to $3,200 annually for upgrades such as heat pumps, insulation, and energy-efficient windows. Specific limits include:
- Heat pumps/biomass stoves: Up to $2,000
- Exterior windows/skylights: $600
- Exterior doors: $250 per door (up to $500 total)
- Electrical panel upgrades: $600
| Improvement Type | Maximum Annual Tax Credit |
|---|---|
| Heat Pumps / Biomass Stoves | $2,000 |
| General Energy Efficiency (Doors, Windows, Insulation) | $1,200 |
| Exterior Doors | $250 per door ($500 total) |
| Exterior Windows and Skylights | $600 |
| Electrical Panel Upgrades | $600 |
Builders may also qualify for the Section 45L New Energy Efficient Home Credit, which offers up to $5,000 for DOE-certified energy-efficient homes purchased before July 1, 2026. ENERGY STAR-certified manufactured homes qualify for a $2,500 credit.
"Energy efficient Tiny House owners... are eligible for the same Federal tax credits, along with States and power utility companies rebates as traditional home owners." - Tiny Off-Grid House Research
State incentives vary widely. For example, Vermont encourages replacing mobile homes with zero-energy modular homes, Maine offers low-interest loans and grants for upgrading older homes, and Oregon provides cash incentives for energy-efficient manufactured homes through the Energy Trust of Oregon. Many local utility companies also offer rebates for energy-efficient equipment, like mini-split heat pumps or electrical panel upgrades, with rebates up to $600.
To take full advantage of these benefits, ensure your prefab tiny home meets ENERGY STAR or DOE Efficient New Home standards. Since these credits are nonrefundable and depend on your tax liability, consulting a tax professional is recommended to determine the best way to apply them over time. For detailed information on federal, state, and utility incentives in your area, visit the Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency (DSIRE).
How to Choose and Buy an Energy-Efficient Prefab Tiny Home
If you're ready to invest in an energy-efficient prefab tiny home, it's essential to approach the process with a clear plan. From understanding your needs to researching builders and finding the perfect home, each step plays a crucial role in ensuring your choice aligns with your lifestyle and energy goals.
Determining Your Needs and Budget
Start by assessing your daily routines, local climate, and whether you prefer a permanent or mobile home. Energy-efficient tiny homes typically range between 120 and 400 square feet, so think about how much space you truly need. Pay attention to how insulation, air sealing, windows, and heating or cooling systems work together to reduce energy consumption. The goal is to create a home where all systems complement each other seamlessly.
When setting your budget, look beyond the initial price tag. Energy-efficient features generally add about 5% to 10% to the base cost of a standard build. However, with federal and state incentives, this premium often drops to 4% to 8%. Downsizing the home’s footprint can also help offset these additional costs.
"A high-performance home can protect you from a rapid rise in energy prices." - U.S. Department of Energy
Focus on the total cost of ownership rather than just the purchase price. Many buyers find that energy-efficient upgrades lower their monthly utility bills enough to cover the slightly higher mortgage payments, resulting in a net-positive cash flow right from the start. Tools like the DSIRE database can help you identify incentives and rebates to further reduce costs.
Researching Manufacturers and Builders
When comparing prefab tiny home manufacturers, prioritize builders with third-party certifications that verify energy performance. Look for homes certified under programs like ENERGY STAR®, DOE Zero Energy Ready Home (ZERH), or Passive House. For mobile tiny homes, certifications such as the "Green Recreational Vehicle" from TRA Certification, Inc. are particularly valuable.
Ask builders about their quality assurance processes. Do they work with recognized inspectors? What type of insulation do they use? Are the windows dual-pane or triple-pane? How do they ensure effective air sealing? These details can make a significant difference in your home's energy efficiency.
High-efficiency mechanical systems and smart energy controls are also essential. Request a Home Energy Score, a national rating system developed by the U.S. Department of Energy, to get a standardized estimate of the home’s energy performance and potential savings.
For inspiration, consider the THIMBY (Tiny House in My Backyard) project by UC Berkeley's Renewable & Appropriate Energy Laboratory. This 18.5 m² home achieved an 88% reduction in site energy use and a 96% drop in carbon emissions compared to a standard 2,100-square-foot home built to 2016 Title 24 standards.
"Optimizing such houses through integration of energy and water saving technologies, home energy management systems, and strong communication between modelers, builders and occupants will be essential to achieving dramatic energy (87%), water (82%), and carbon (96%) savings." - Alana Bowen Siegner, RAEL Berkeley
As of August 2024, Tumbleweed Tiny House Company earned top-level green certification from TRA Certification, Inc. Their homes feature HRV systems, recycled non-emitting insulation, and low-flow water fixtures.
Finding Your Home on Nomad Adjacent
Once you’ve outlined your energy and performance criteria, head to Nomad Adjacent (https://nomadadjacent.com) to simplify your search. This platform offers a map-based tool that allows you to filter homes by location, size, and specific features, helping you find options that meet your energy-efficiency requirements.
The site connects you directly with builders specializing in certified, customizable tiny homes. You’ll find everything from shell models - ideal for personalizing with your own energy-efficient upgrades - to fully finished, move-in-ready homes complete with integrated appliances and furniture. Custom builds typically start at $90,000, with lead times of 2 to 3 months. Options like solar panels, battery storage, and advanced insulation systems can be added to meet net-zero energy goals.
Before finalizing a purchase, conduct an energy load audit. This step helps you estimate your daily and seasonal energy needs, ensuring solar systems or battery storage (like Tesla Powerwall) are appropriately sized. Early coordination with local code officials and your utility company is crucial to avoid costly changes during installation, whether your home is stationary or mobile.
"Early coordination with code officials and the utility avoids costly changes during construction." - Articru Scribes, Zero-Energy Tiny House
Nomad Adjacent also allows you to communicate directly with sellers and builders. Before sealing the deal, request documentation that confirms the manufacturer conducts blower-door testing to identify and fix potential air leaks. This ensures your home will deliver the energy performance you’re counting on for years to come.
Conclusion
Energy-efficient prefab tiny homes offer a mix of financial savings, reduced environmental impact, and a simpler, more intentional way of living. By transitioning to a tiny home, you can cut energy consumption and significantly lower your carbon footprint. For example, these homes emit just 2,000 pounds of CO₂ annually compared to the 28,000 pounds from a standard-sized house - a striking 92% reduction. Plus, they can slash utility bills by as much as 60%–90% each year.
While the upfront costs might seem steep, incentives and the dramatic drop in utility expenses often balance things out over time. Many homeowners even report seeing immediate financial benefits, as lower utility bills offset slightly higher mortgage payments from the start. Beyond the numbers, tiny homes simplify life by reducing maintenance needs and eliminating clutter, freeing up time for what truly matters.
"Waste is ugly; efficiency is beautiful." - Jay Shafer, Founder of the tiny house movement
Another advantage lies in their factory-built design. Prefab construction ensures consistent quality, minimizes material waste, and speeds up assembly by avoiding weather-related delays. Whether you're drawn to the mobility of a wheeled model or the permanence of a foundation-based unit, these homes offer the flexibility and independence that appeal to today’s homeowners.
For those ready to explore this lifestyle, platforms like Nomad Adjacent can help you find the perfect fit. Their map-based search and direct connections to builders make it easy to discover certified, customizable options - from shell models ideal for DIY enthusiasts to fully finished homes equipped with solar panels and smart technology.
FAQs
What are the key advantages of choosing a prefab tiny home over a traditional house?
Prefab tiny homes come with a host of advantages over traditional houses. For starters, they’re easier on your wallet - lower upfront costs and reduced utility bills make them an attractive option. Thanks to their smaller size and energy-efficient designs, these homes help you save money while minimizing your environmental footprint.
Another big perk? Speed. Prefab homes are constructed in factory-controlled settings, which means they’re built much faster than traditional homes. This process also cuts down on delays and material waste, making it a more streamlined way to build.
Many of these homes are also designed with eco-conscious living in mind. Features like high-performance insulation and optional renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, make them a smart choice for anyone looking to reduce their energy use. Their compact design only adds to their efficiency, offering a greener, more economical way to live in today’s world.
How do energy-efficient prefab tiny homes achieve net-zero energy use?
Energy-efficient prefab tiny homes reach net-zero energy use by blending thoughtful design with cutting-edge technology. These homes are built to minimize energy needs with features like airtight, highly insulated walls - often using structural insulated panels (SIPs) - along with energy-efficient windows and passive solar design principles. Systems such as heat pump HVAC units, energy recovery ventilators, and LED lighting further lower energy consumption.
To balance out any remaining energy use, many of these homes include on-site renewable energy solutions, such as solar panels combined with battery storage. This setup enables them to produce as much energy as they use over the course of a year, achieving true net-zero energy efficiency.
What are the financing options for buying an energy-efficient prefab tiny home?
If you're considering buying an energy-efficient prefab tiny home, you’ve got a few financing routes to explore. Two popular options are personal loans and RV loans, especially if your tiny home is on wheels and doesn’t have a permanent foundation. If you already own a home, tapping into your property’s equity through a home equity loan or a HELOC can also be a smart way to secure funds.
For tiny homes with energy-saving features, options like Energy-Efficient Mortgages (EEMs) or programs from Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac might offer better loan terms, thanks to the lower utility costs these homes typically bring. Some banks and credit unions also provide construction loans for prefab builds or renovation loans specifically designed for energy-efficient upgrades.
To simplify the process, platforms like Nomad Adjacent can connect you with lenders who understand the unique requirements of financing tiny homes. This can help you find a solution that aligns with your budget while letting you enjoy the long-term savings of an energy-efficient lifestyle.